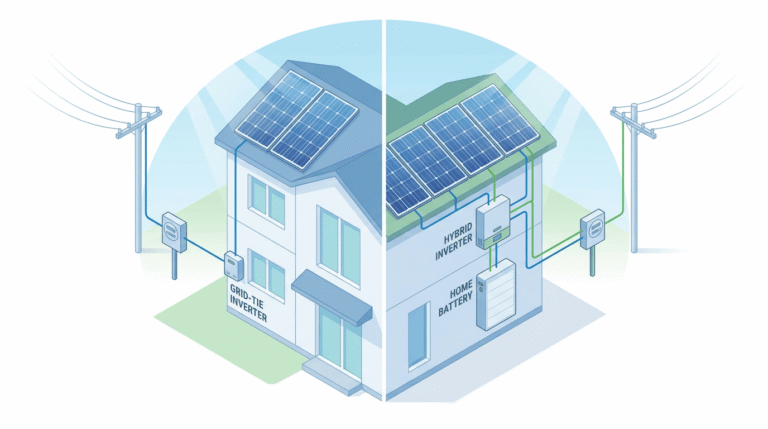
As an engineer and procurement specialist who has been deeply embedded in the new energy sector for over a decade, I’ve witnessed the transformative power of technology firsthand. Among the most pivotal advancements is the rise of energy storage batteries. These are not merely components; they are the linchpin of the global energy transition. Nowhere is this more apparent than in the Asia-Pacific region, a dynamic and rapidly expanding epicenter for the energy storage market. The synergy between burgeoning economies, ambitious renewable energy targets, and the critical need for grid stability has created a perfect storm, positioning the Asia-Pacific region as the most promising frontier for energy storage batteries.
This comprehensive analysis will delve into the market prospects for energy storage batteries in the Asia-Pacific region. We will explore the primary drivers fueling this exponential growth, dissect the challenges and obstacles that lie ahead, and identify the most compelling development trends and investment opportunities. For businesses, investors, and policymakers, understanding the nuances of the Asia-Pacific energy storage market is not just advantageous—it’s essential for navigating the future of energy.
The Growth Engine: Why the Asia-Pacific Energy Storage Battery Market is Surging

The Asia-Pacific region is on track to become the world’s largest energy storage market, a forecast supported by numerous industry analyses. According to a report from Wood Mackenzie, the cumulative energy storage capacity in the Asia-Pacific region is projected to reach 728 GWh by 2032, a testament to the surging demand. This insatiable appetite for energy storage batteries stems from the region’s unique position as a global hub for both manufacturing and population growth. Countries like China, Japan, South Korea, India, and Australia are at the forefront, where battery technology is no longer a niche solution but a cornerstone of national energy strategy. The core mission is the energy transition—moving away from fossil fuel dependency towards a cleaner, more resilient, and decentralized energy infrastructure. In this paradigm shift, energy storage batteries are the enabling technology, providing the flexibility and reliability that modern power grids demand.
The demand for these energy storage products is multifaceted, ranging from large-scale, grid-level energy storage systems designed to stabilize national power supplies to commercial and residential applications that empower consumers with energy independence. This burgeoning Asia-Pacific energy storage market is not a monolithic entity but a complex tapestry of diverse needs, policies, and technological landscapes, all pointing towards a future where energy storage batteries play a central role.
Key Drivers Fueling the Asia-Pacific Energy Storage Battery Market
The remarkable growth trajectory of the energy storage battery market in the Asia-Pacific region is not accidental. It is propelled by a confluence of powerful, interconnected factors that create a self-reinforcing cycle of demand and innovation.
1. Proactive Policy and Government Incentives
Governments across the Asia-Pacific region have recognized the strategic importance of energy storage batteries and are actively fostering market development through robust policy frameworks. These incentives are critical in de-risking initial investments and accelerating deployment.
China: As the undisputed leader, China has integrated energy storage into its national development strategy. The 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) explicitly calls for the large-scale development of new energy storage systems. This is backed by provincial-level subsidies, mandates for renewable energy projects to be co-located with storage (often 10-20% of the generation capacity), and streamlined approval processes. This top-down approach has supercharged the Asia-Pacific battery technology landscape.
India: With its ambitious goal of reaching 500 GW of non-fossil fuel energy capacity by 2030, India faces immense grid integration challenges. The government has responded with initiatives like the National Energy Storage Mission and production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes to encourage domestic manufacturing of energy storage batteries, reducing reliance on imports and fostering a local ecosystem.
Australia: A world leader in rooftop solar penetration, Australia sees energy storage batteries as essential for grid stability. State-level schemes, such as subsidies for residential batteries and tenders for large-scale “big battery” projects, are driving rapid adoption in both behind-the-meter and front-of-the-meter segments.
Japan and South Korea: These technologically advanced nations are focusing on energy storage batteries to enhance energy security and support their high-tech manufacturing industries. Subsidies are available for commercial and industrial users to install energy storage systems for peak shaving and emergency backup power.
2. The Explosive Growth of Renewable Energy
The Asia-Pacific region is a global leader in renewable energy deployment, particularly solar and wind. However, the intermittent nature of these sources—the sun doesn’t always shine, and the wind doesn’t always blow—poses a significant challenge to grid stability. Energy storage batteries are the definitive solution to this problem. They act as a buffer, absorbing excess energy during periods of high generation and dispatching it when production wanes. This “time-shifting” capability is crucial for ensuring a reliable power supply. The proliferation of solar and wind farms across China, India, and Australia directly translates into a massive, built-in demand for co-located energy storage systems, making renewable energy integration arguably the single most significant driver for the energy storage market.
3. Escalating Electricity Demand
Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and rising living standards across much of the Asia-Pacific region are leading to a sharp increase in electricity consumption. Furthermore, the burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) market adds another substantial layer of demand on the grid. This growth puts immense strain on existing power infrastructure. Energy storage batteries help manage this strain by providing peak-shaving services—charging during off-peak hours when electricity is cheap and discharging during peak demand periods. This not only defers the need for costly upgrades to transmission and distribution networks but also enhances overall grid efficiency. The link between the region’s economic growth and the need for energy storage batteries is direct and undeniable.
4. The Critical Need for Grid Stability and Resilience
Many parts of the Asia-Pacific region, particularly developing nations like the Philippines, Indonesia, and parts of India, grapple with aging grid infrastructure and frequent power outages. For these countries, energy storage batteries are not just about energy transition; they are about energy security and economic continuity. Energy storage systems can provide essential ancillary services, such as frequency regulation and voltage support, to stabilize the grid in real time. They also form the backbone of microgrids, which can operate independently during a wider grid failure, ensuring that critical facilities like hospitals, data centers, and manufacturing plants remain operational. This resilience factor is a powerful driver for the adoption of energy storage batteries across the commercial and industrial sectors.
Hurdles and Headwinds: Challenges Facing the APAC Energy Storage Market
Despite the immense potential, the path to widespread adoption of energy storage batteries in the Asia-Pacific region is not without its obstacles. Stakeholders must navigate a complex landscape of economic, technical, and regulatory challenges.
1. High Initial Investment Costs
From a procurement perspective, the most significant barrier remains the high upfront capital expenditure (CAPEX) for energy storage systems. While costs have fallen dramatically over the past decade, a utility-scale battery project can still represent a multi-million dollar investment. For smaller businesses and residential customers in developing economies, the initial outlay can be prohibitive. The long-term benefits, such as lower electricity bills and energy security, are compelling, but the initial financial hurdle is substantial. Overcoming this requires innovative financing models, government subsidies, and continued technological advancements to drive down the Levelized Cost of Storage (LCOS).
2. Technological Maturity and System Integration
While battery technology is advancing rapidly, challenges related to integration, safety, and performance remain. The Asia-Pacific region sees a wide variety of environmental conditions, from extreme heat and humidity in Southeast Asia to colder climates in other parts. Ensuring that energy storage batteries, particularly their Battery Management Systems (BMS) and thermal management systems, can perform reliably and safely across these diverse conditions is a complex engineering challenge. Furthermore, integrating energy storage systems with different grid codes, communication protocols, and legacy infrastructure across various countries requires deep technical expertise. The risk of thermal runaway and battery fires, though rare, is a significant concern that necessitates stringent safety standards and quality control throughout the supply chain.
3. Market Acceptance and Consumer Education
In many parts of the Asia-Pacific region, awareness and understanding of energy storage batteries among the general public and even some businesses are still low. There is a critical need for education on the benefits, operational principles, and safety aspects of energy storage products. Building consumer trust requires transparent communication, strong warranties, reliable after-sales service, and showcasing successful case studies. Without this foundational market education, achieving the full potential of distributed energy resources (like residential batteries) will be challenging.
4. Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty
While many governments are supportive, the regulatory landscape can be fragmented and inconsistent across the Asia-Pacific region. A lack of standardized interconnection procedures, unclear permitting processes, and the absence of well-defined market mechanisms for valuing the services provided by energy storage batteries (like frequency regulation) can create uncertainty for investors. A clear, stable, and long-term policy framework is essential to attract the massive investment required to scale the Asia-Pacific energy storage market. Harmonizing standards and regulations across the region could further accelerate growth.
The Future Unveiled: Development and Investment Opportunities
Looking ahead, the outlook for the energy storage battery market in the Asia-Pacific region is exceptionally bright. The convergence of falling costs, technological innovation, and escalating demand is unlocking a wealth of investment opportunities.
1. Sustained Market Growth Projections
Authoritative sources unanimously predict robust and sustained growth. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has highlighted that energy storage deployment needs to expand significantly to meet climate goals, with the Asia-Pacific region being a key driver of this expansion. The market for energy storage batteries is expected to grow exponentially, particularly in China, which is projected to account for a substantial share of global installations. India and Southeast Asian nations are seen as the next wave of hyper-growth markets. This growth will not be confined to utility-scale projects; the commercial, industrial, and residential sectors are also poised for significant expansion, creating diverse opportunities across the value chain.
2. Technology-Driven Cost Reduction
As an engineer, this is the most exciting frontier. Continuous innovation in battery technology is the primary catalyst for cost reduction. The shift towards Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) chemistry for stationary storage applications has already lowered costs and improved safety compared to Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) chemistries. Beyond lithium-ion, research into alternative technologies like sodium-ion batteries and flow batteries promises further cost reductions and diversification of the supply chain. Simultaneously, advancements in manufacturing processes, automation, and economies of scale are relentlessly driving down the price per kilowatt-hour. This downward cost trajectory is the key to unlocking mass-market adoption of energy storage batteries.
3. Deep Integration with Renewable Energy
The most significant market opportunity lies in the synergy between energy storage batteries and renewable energy. “Solar-plus-storage” and “wind-plus-storage” projects are becoming the new standard. These hybrid projects offer dispatchable, clean energy, making them competitive with traditional fossil fuel power plants. This creates opportunities not just for battery manufacturers but also for project developers, EPC (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction) firms, and software providers who specialize in energy management systems (EMS) that optimize the interaction between generation and storage. The rise of Virtual Power Plants (VPPs), which aggregate distributed energy storage systems to provide grid services, represents another lucrative, high-tech frontier.
4. The Untapped Potential of Emerging Markets
While China, Japan, and Australia are the current leaders, the long-term growth story of the Asia-Pacific energy storage market will be written in its emerging economies. Countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Thailand are characterized by rapid GDP growth, rising energy needs, and a pressing need to improve grid reliability. For these nations, energy storage batteries offer a way to leapfrog traditional grid infrastructure development. They can facilitate the deployment of utility-scale renewables and support the creation of resilient microgrids in remote or island communities. These markets represent a greenfield opportunity for investors and companies willing to navigate their unique local challenges.
Conclusion: Navigating the Bright and Challenging Future of APAC's Energy Storage Market
The journey for energy storage batteries in the Asia-Pacific region is at an inflection point. The market is transitioning from a nascent stage to a phase of explosive, mainstream growth. The convergence of supportive government policies, the relentless expansion of renewable energy, and the fundamental need for a stable and reliable power supply has laid a rock-solid foundation for the future of the energy storage market.
Policy Support Remains Paramount: The continued commitment of governments will be the critical enabler. Financial incentives, clear regulatory pathways, and investment in grid modernization are essential to maintain the current momentum.
Technology and Cost are the Breakthrough Levers: From an engineering and procurement standpoint, the future hinges on technological breakthroughs and cost reductions. As battery technology matures and manufacturing scales, energy storage batteries will become the undisputed core solution for the energy challenges facing the Asia-Pacific region.
Collaboration is Key: The complexity of the energy storage market necessitates a collaborative approach. Success will be driven by partnerships between technology providers, project developers, investors, and utilities. By working together to innovate, standardize, and educate, the industry can overcome the existing barriers and unlock the full potential of energy storage batteries.
For any stakeholder in the global energy sector, the message is clear: the Asia-Pacific region is the definitive growth frontier for energy storage batteries. The challenges are real, but the opportunities are immense. The time to engage, invest, and innovate in the Asia-Pacific energy storage market is now.